How do we hear?
What is Sound?
Sound is a vibration that travels through solid, liquid or a gas and can be heard when they reach a person's ear. Sound is created by a vibrating object.
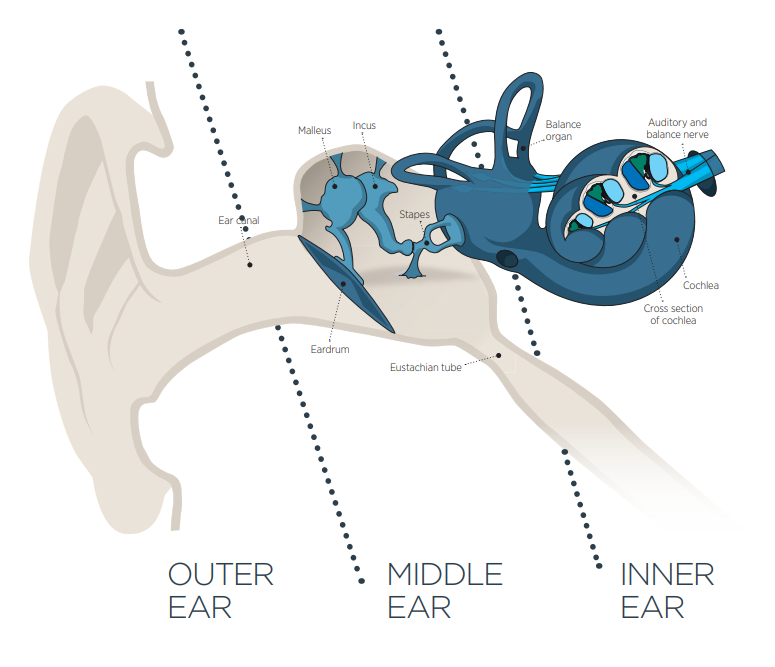
The human ear is a very complex organ. It not only transmits the vibrations to brain but also helps in balancing. It has three main areas the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Each part plays unique role in transmitting sound to brain so we can hear.
The Outer Ear
Outer ear includes pinna and ear canal. Pinna acts like a funnel and directs the sound waves to the ear canal. Pinna also helps us to identify which direction the sound comes from.
The Middle Ear
The sound waves from ear canal hits the ear drum. The ear drum then vibrates and sends the vibrations to three tiny bones called malleus, incus and stapes. These tiny bones amplify the sound waves and send them to cochlea.
The Inner Ear
The inner ear consists of Cochlea (which helps in hearing ) and semicircular canals (which helps in balancing). Sound vibration causes the fluid inside the cochlea to ripple and the hair cells starts to move which then converts such movements to electrical signals. These signals are then transferred through auditory nerve to brain. The brain processes the sound and helps in separating meaningful speech from noise.